OPTIMAL FAIR
The CMRR software downloads have migrated to a new site!
If you have not visited this page since Dec 26, 2025, you will need to reset your password. Your username is the email address that you used to sign the University of Minnesota license agreement.
Please be aware that while Siemens C2P agreements are for the specific scanner+institution, the University of Minnesota license agreement to download sequences on this site is for an individual. If your institution needs to change or add additional authorized people to download sequences, each person will need to sign the license agreement and then CMRR will create an account on this site.
FAIR ASST and OPTIMAL FAIR perfusion imaging methods were two variants of the widely used pulsed arterial spin labeling (PASL) method, FAIR (Flow-sensitive Alternating Inversion Recovery), to better facilitate non-contrast enhanced brain perfusion imaging applications. These methods were first developed at UT Southwestern Medical Center and further improved/upgraded at CMRR.
Background
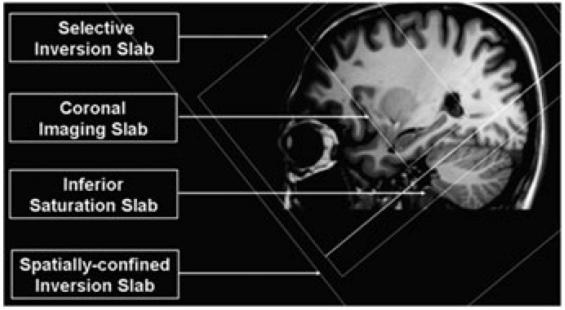
Arterial spin labeling (ASL) measurements of blood flow in human hippocampus are complicated by its relatively small size and unusual shape. The diameter of the human hippocampus tapers posteriorly along its 45–50-mm curved length from a relatively wide head (8–12 mm) to a thinner body (6–8 mm) and even thinner tail (2–6 mm). The coarse spatial resolution (isotropic 3.5-mm voxels) of standard ASL imaging limited the number of voxels that could be sampled without partial volume effects where the narrow aspects of the body and tail of the hippocampus curved through the slice planes, hindering the ability to conclusively characterize and distinguish middle and posterior regions. To overcome these limitations, a standard FAIR (Flow-sensitive Alternating Inversion Recovery) pulse sequence was modified by rotating the imaging slice plane orthogonal to the oblique axial plane of the tagging inversion. With this Orthogonally Positioned Figure 1 Spatial definitions of different slabs Tagging Imaging Method for Arterial Labeling with FAIR (OPTIMAL FAIR) technique, oblique coronal imaging slices with high in-plane resolution can be placed perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the hippocampus along the A–P direction (Figure 1). This reduces partial volume effects and increases resolution, allowing the detection of finer details of the A–P differences in perfusion parameters, thus enabling reliable studies of these perfusion differences in both normal and compromised or diseased hippocampus (1-3).
Features
- The OPTIMAL FAIR sequence contains a sequence module for temporal bolus width definition by using either QUIPSS II or Q2TIPS methods, and these two methods can also be turned off when the number of saturation pulses (via user interface (UI) parameter “QSAT.No.”) is set to zero.
- Imaging slab pre-saturation is supported with two execution modes: a single saturation before ASL inversion RF pulses or one pre-inversion saturation combined with two post-inversion saturation and minimize the subtraction errors caused by the imperfect inversion profile (4).
- HSN RF pulse (N>= 4) can be selected for FAIR inversions to reduce RF peak power that is usually limited at ultra high fields, e.g. 7T.
- Both QUIPSS II and Q2TIPS are supported with great flexibility via multiple UI parameters: the number, duration, slab size and temporal gaps of saturation RF (please refer Figure 1 in the reference 4).
- Up to two M0 images can be acquired at the end of ASL series acquisition.
- Bi-polar flow-encoding/crushing gradients are available to suppress hyperintense intravascular signals.
Example
License
Obtaining a license
The available supported software versions are listed below. If you are interested in obtaining these sequences, please follow this process to obtain a CMRR license:
- Obtain authorization from your Siemens Regional Collaboration Manager for the specific software you would like to license.
- Contact your Siemens Regional Collaboration Manager for authorization. Please ask them to use the following text in the agreement: "developed by Dr. Xiufeng Li and colleagues (“DEVELOPER”), employees of the University of Minnesota." If you are experiencing any delays working with your Siemens Regional Collaboration Manager please contact Colin Giambrone (colin.giambrone@siemens-healthineers.com).
- Send the completed authorization form to Xiufeng Li
- Select the license from the OTC website and complete the license agreement.
- CMRR will send you your account information.
Please note that the entire licensing process may take up to two weeks to process.
Once you have executed a C2P agreement and have been given an access password, the sequence binaries can be downloaded from the Download link(s) below by selecting the desired release number.
Note: The C2P agreement in step 1 applies to the institution (scanner), whereas the University of Minnesota license agreement in step 2 applies to an individual. If someone else at your institution has historically been the download contact for sequences and you would also like download access, please sign the University of Minnesota license agreement and CMRR will create a download account for you.
Citation
UPDATE_ME
Li X, et al. Anteroposterior perfusion heterogeneity in human hippocampus measured by arterial spin labeling MRI. NMR Biomed. 2013; 26:613-21. doi: 10.1002/nbm.2898
Li X, et al. Dynamic physostigmine effects on hippocampus perfusion. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012; 35:280-6. doi: 10.1002/jmri.22821
Li X, et al. Hippocampal dysfunction in Gulf War veterans: investigation with ASL perfusion MR imaging and physostigmine challenge. Radiology. 2011; 261:218-25. doi: 10.1148/radiol.11101715
Contact
If you have noticed a bug or have a request for a new feature in a future release, please contact Xiufeng Li. Be sure to include the sequence variant and the model of scanner you are using in the problem description.
Download
References
- Li X, et al. Anteroposterior perfusion heterogeneity in human hippocampus measured by arterial spin labeling MRI. NMR Biomed. 2013; 26:613-21. doi: 10.1002/nbm.2898
- Li X, et al. Dynamic physostigmine effects on hippocampus perfusion. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2012; 35:280-6. doi: 10.1002/jmri.22821
- Li X, et al. Hippocampal dysfunction in Gulf War veterans: investigation with ASL perfusion MR imaging and physostigmine challenge. Radiology. 2011; 261:218-25. doi: 10.1148/radiol.11101715
- Li X, et al. Improved quantification of brain perfusion using FAIR with active suppression of superior tagging (FAIR ASST). J Magn Reson Imaging. 2011; 34:1037-44. doi: 10.1002/jmri.22734
- Li X, et al. Theoretical and experimental evaluation of multi-band EPI for high-resolution whole brain pCASL Imaging. Neuroimage. 2015; 106:170-81. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.10.029
Staff Login